How to Make Slime? Creating slime is not just a popular activity for kids; it’s a fascinating exploration of chemistry and sensory play that captivates people of all ages. This article dives into the science of slime, offering expert insights and step-by-step instructions on making various types of slime. We’ll also touch on the history of slime and provide answers to frequently asked questions.
Understanding How to Make Slime
Slime is a non-Newtonian fluid that exhibits properties of both solids and liquids under different conditions, thanks to its polymer structure. The primary ingredient in most slime recipes is polyvinyl acetate (PVA), found in school glue, which bonds with borates in borax or boric acid in contact lens solutions, creating the slime’s unique texture.
Step-by-Step Guide to Making Slime
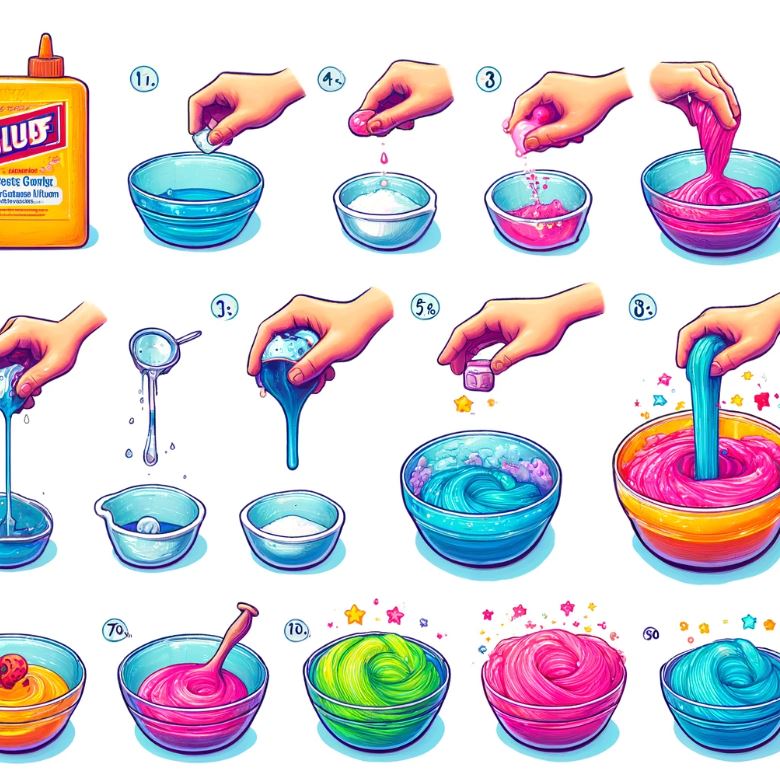
- Basic Slime Recipe (Source: I Heart Naptime)
- Mix Elmer’s white school glue with baking soda in a bowl.
- Add food coloring if desired.
- Gradually mix in saline solution until the mixture reaches your preferred consistency.
- Knead the slime until smooth.
- Fluffy Slime Recipe (Source: One Little Project)
- Combine glue, shaving cream, and food coloring.
- Add borate-containing contact lens solution as the activator.
- Knead until fluffy and no longer sticky.
- Clear Slime Recipe (Source: The Craft Patch Blog)
- Dissolve borax in hot water for the activator.
- Mix clear school glue with water and food coloring.
- Gradually add the borax solution until the slime thickens.
- Butter Slime Recipe (Source: The Craft Patch Blog)
- Follow the basic steps for making slime.
- Incorporate Model Magic clay to achieve a soft, buttery texture.
FAQs about How to Make Slime
- Can slime be made without glue? Yes, slime can be made without glue by using alternatives like cornstarch and dish soap or conditioner for a different texture (The Craft Patch Blog).
- What makes slime fluffy? Adding shaving cream to the slime mixture makes it fluffy (One Little Project).
- How do you color slime? You can use food coloring or acrylic paint to add color to your slime (One Little Project).
- How do I make my slime less sticky? Adding more of your activator (borax solution, contact lens solution) will reduce stickiness (I Heart Naptime).
- How should slime be stored? Slime is best stored in an airtight container to prevent it from drying out (The Craft Patch Blog).
- Is slime safe for all ages? While slime is safe for external play, it should not be ingested. Adult supervision is recommended for young children.
- Can you make slime with just water, salt, and glue? Recipes typically require an activator like borax, contact lens solution, or liquid starch in addition to glue and water.
- What’s the best slime activator? Borax solution, contact lens solution containing boric acid, and liquid starch are among the most effective activators.
- How long does homemade slime last? Properly stored in an airtight container, slime can last several weeks.
- Can slime be made without borax? Yes, recipes using contact lens solutions or liquid starch as activators are effective alternatives to borax.
Detailed Questions
- What is the scientific principle behind slime? Slime demonstrates the properties of polymers and viscoelasticity. When PVA from glue interacts with borates, it forms long chains of molecules, creating a stretchy and moldable substance. The process illustrates cross-linking, where polymer chains are connected, transforming a liquid into a more solid-like material that can still flow.
- How has the popularity of slime evolved over time? Initially popular in the 1970s as a toy product, slime gained resurgence in the 2010s through social media. This revival emphasized DIY aspects, leading to the exploration of various recipes and the educational side of slime-making in understanding chemistry and material science.
- What are the environmental considerations of making and disposing of slime? The sustainability of slime depends on the ingredients used. Slime made with biodegradable substances like food coloring or natural starches poses less of an environmental impact. Proper disposal involves throwing it in the trash, as washing slime down the drain can cause blockages due to its viscosity and composition.
- How can slime-making be integrated into educational activities? Slime-making offers a hands-on experience for learning about scientific concepts like chemical reactions, states of matter, and material properties. It can be used in classrooms to engage students in experiments that demonstrate theseconcepts of polymer science, the behavior of non-Newtonian fluids, and the principle of chemical bonding. It can foster curiosity and encourage experimentation, allowing students to modify recipes to see how changes in ingredients affect the slime’s properties, thus promoting critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- What are the safety precautions to consider while making slime at home? Safety is paramount when making slime, especially with young children involved. Non-toxic ingredients should be chosen, and products like borax should be handled by adults or under strict supervision, as improper use can lead to skin irritations or other health issues. Additionally, ensuring the workspace is clean and equipped with non-food utensils for mixing can prevent cross-contamination.
- Safety Measures:
- Use non-toxic, safe ingredients for children.
- Adult supervision for young children, especially when using chemicals.
- Avoid ingestion and ensure hand washing after play.
- Keep slime away from pets.